When it comes to automotive safety, airbags are often considered lifesaving devices. Yet, the Takata airbag scandal, one of the most significant recalls in automotive history, highlights how cutting corners in manufacturing can lead to catastrophic outcomes. This saga, marked by explosive airbags and a global recall, offers valuable lessons for industries worldwide.
Who Was Takata?
Founded in 1933, Takata Corporation started its journey as a humble textile manufacturer in Japan. By the 1960s, the company shifted its focus toward automotive safety, manufacturing seat belts. Over the years, Takata expanded its portfolio, introducing child safety seats and airbags, cementing its reputation as a leader in the global automotive safety market.
In the 1980s, Takata pioneered airbag technology and rapidly gained recognition among automakers. By the early 2000s, its products were being used in vehicles manufactured by major brands, including Honda, Toyota, Ford, and General Motors. However, this dominance came with its challenges, as the company eventually prioritized cost-efficiency over safety.
What Happened in the Takata Airbag Scandal?
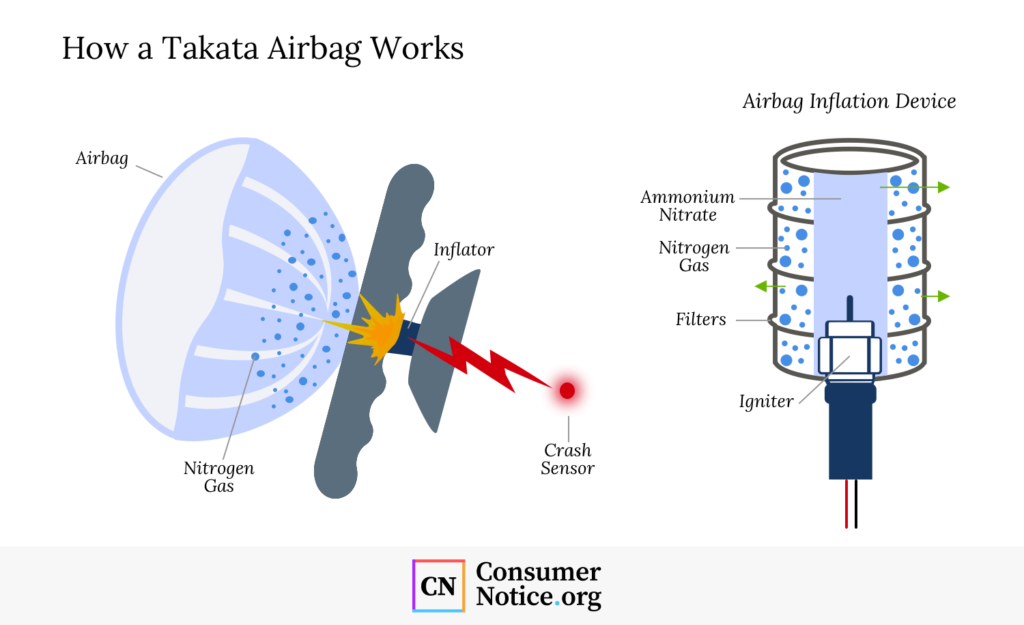
At the heart of the Takata scandal was a faulty airbag inflator that had the potential to rupture during deployment. The problem arose from the use of ammonium nitrate, a volatile compound that deteriorates under temperature fluctuations and exposure to moisture.
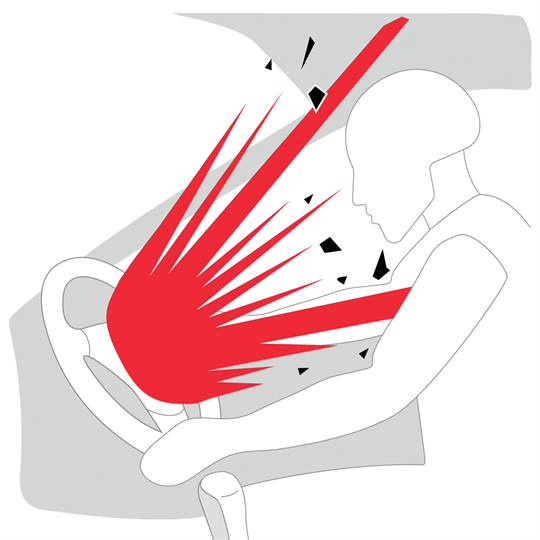
When the airbag deployed, the unstable chemical caused the inflator to explode, sending metal shrapnel into the vehicle cabin. Instead of saving lives, these defective airbags caused severe injuries and even fatalities.
How Did It Happen?
Takata’s decision to use ammonium nitrate was primarily driven by cost-cutting measures. The company opted for this cheaper chemical instead of safer but costlier alternatives like guanidine nitrate. Unfortunately, Takata’s testing processes failed to account for the long-term stability of ammonium nitrate, particularly in regions with high humidity and extreme temperatures.
The instability of the chemical led to the degradation of the inflators, turning them into ticking time bombs. Over time, the defective airbags were linked to numerous injuries and fatalities, sparking an unprecedented global recall.
A Timeline of the Takata Airbag Scandal
The Takata airbag crisis unfolded over nearly two decades. Here’s a detailed timeline of key events:
2004: Early Warning Signs
The first reported incident occurred in Alabama when a Honda vehicle’s airbag exploded, injuring the driver. Takata and Honda dismissed the incident as a one-off issue.
2008: Initial Recalls Begin
Honda issued the first recall of Takata airbags, citing potential defects. The recall involved 4,000 vehicles, but the scope soon expanded as more cases surfaced.
2013-2014: A Growing Problem
Automakers such as Toyota, Nissan, BMW, and Ford joined the recall efforts. Investigations revealed that millions of vehicles were equipped with defective Takata airbags.
2015: Regulatory Intervention
The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) imposed a record $70 million fine on Takata for failing to promptly disclose the defects. Takata was also required to phase out ammonium nitrate in its inflators.
2016: Death Toll Rises
By this year, at least 11 fatalities and over 100 injuries were directly linked to Takata airbag inflator ruptures. The global recall expanded to 70 million vehicles in the U.S. alone.
2017: Bankruptcy and Acquisition
Takata filed for bankruptcy due to mounting lawsuits and recall costs. It was acquired by Key Safety Systems, which rebranded as Joyson Safety Systems.
2024: A Grim Legacy
As of this year, 28 confirmed deaths in the U.S. and hundreds of injuries have been linked to defective Takata airbags. The recall remains ongoing, with millions of vehicles still unrepaired.
The Fallout
The Takata airbag recall is the largest in automotive history, involving over 100 million vehicles globally. The scandal not only led to Takata’s bankruptcy but also tarnished the reputations of automakers that used its products.
For consumers, the scandal caused fear and frustration. Millions of vehicle owners were forced to wait for replacements as manufacturers scrambled to meet demand. The financial and logistical burden on automakers was immense, with recall costs running into billions of dollars.

Lessons Learned
The Takata airbag scandal offers critical lessons for manufacturers, regulators, and consumers alike. Here are some key takeaways:
1. The Perils of Cost-Cutting
Takata’s decision to use ammonium nitrate was driven by a desire to reduce costs. However, this decision backfired, leading to a massive loss of life and financial ruin for the company. Manufacturers must recognize that compromising on safety to save money can have dire consequences.
2. Importance of Rigorous Testing
The instability of ammonium nitrate was a known issue, yet Takata failed to conduct adequate long-term testing. This oversight highlights the need for thorough research and testing, particularly for products that directly impact consumer safety.
3. Transparency Is Key
Takata initially downplayed the severity of the problem, delaying recalls and eroding public trust. Companies must be transparent about potential safety issues and take proactive steps to address them.
4. Role of Regulatory Oversight
The NHTSA played a critical role in holding Takata accountable and ensuring that affected vehicles were recalled. Robust regulatory oversight is essential to prevent similar incidents in the future.
The Human Cost
Beyond the financial and logistical challenges, the Takata airbag scandal had a devastating human cost. Victims suffered horrific injuries, including loss of eyesight and severe lacerations, while families mourned loved ones who lost their lives.
One notable case was that of Huma Hanif, a 17-year-old girl who died when the airbag in her Honda Civic ruptured during a minor accident. Her tragic death underscores the life-and-death stakes of automotive safety.
A Global Recall: Where Are We Now?
The Takata airbag recall is far from over. Millions of vehicles equipped with defective airbags remain on the road, posing a continued risk to drivers and passengers. Automakers and regulators continue to urge consumers to check whether their vehicles are part of the recall and to replace defective airbags promptly.
To facilitate this process, the NHTSA launched the Takata Recall Spotlight, an online tool that allows consumers to check their vehicle identification numbers (VINs) for recall status. Despite these efforts, the recall completion rate remains low, particularly in older vehicles.
How to Avoid Similar Catastrophes
The Takata airbag scandal serves as a sobering reminder of the importance of prioritizing safety in manufacturing. Here are some strategies to prevent similar incidents in the future:
1. Emphasize Ethical Decision-Making
Companies must balance profitability with ethical considerations. Decisions that prioritize short-term gains over long-term safety can lead to disastrous outcomes.
2. Invest in Quality Control
Robust quality control processes can help identify potential issues before they escalate. This includes conducting comprehensive testing and using high-quality materials.
3. Foster a Culture of Accountability
Organizations should encourage employees to speak up about safety concerns and establish mechanisms for addressing these concerns effectively.
4. Strengthen Industry Standards
Regulators and industry groups should collaborate to develop stringent safety standards and ensure compliance through regular audits.
Conclusion
The Takata airbag scandal is a cautionary tale of what can happen when cost-cutting and negligence overshadow safety and ethics. While the recall continues to affect millions of consumers worldwide, the lessons learned from this tragedy have prompted changes in how automotive safety is approached.
For consumers, the message is clear: stay informed about recalls and take action to address safety issues promptly. For manufacturers, the Takata case underscores the critical importance of prioritizing safety, transparency, and accountability in every aspect of the production process. Let this be a reminder that in the pursuit of innovation, human lives must always come first.
References
The following sources were consulted to gather accurate and comprehensive information for this blog post:
- The History of the Takata Airbag Recall – GetJustice.com
- From Textile Maker to Airbag Giant: The Rise and Fall of Takata – Hindustan Times
- Takata Air Bag Scandal Timeline – USA Today
- Takata Recall Spotlight – NHTSA
- What to Know About the Takata Airbag Recall – WilliamMattar.com
- Takata Airbag Recall: Everything You Need to Know – Consumer Reports
- When Airbags Don’t Save Lives: The Takata Story – Automotive IQ
- The Complete Story of Takata Airbags and the Biggest Recall Ever – Jalopnik
- Why Us – MBP India