In recent years, metal 3D printing has emerged as a revolutionary technology, offering unprecedented capabilities in manufacturing and design. As with any technology, it has its pros and cons. In this blog post, we’ll delve into the intricacies of metal 3D printing, exploring its benefits and drawbacks to provide a balanced view. Whether you’re a manufacturing professional or an enthusiast, this guide will help you understand the potential of metal 3D printing.
What is Metal 3D Printing?
Metal 3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a process where metal parts are built layer by layer from a digital file. This method contrasts with traditional subtractive manufacturing, where the material is removed to create the final product. Technologies used in metal 3D printing include Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS), Electron Beam Melting (EBM), and Binder Jetting.
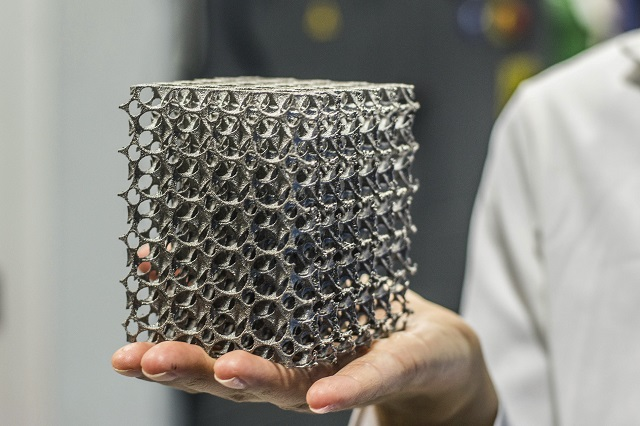
The Pros of Metal 3D Printing
1. Design Freedom
One of the most significant advantages of metal 3D printing is the freedom it offers in design. Complex geometries, which would be impossible or very costly to achieve with traditional manufacturing methods, can be easily created. This capability allows for the production of lightweight structures, optimized for strength and material use.
2. Reduced Waste
Traditional manufacturing processes often involve significant material wastage. Metal 3D printing, on the other hand, builds parts layer by layer, using only the material necessary for the part. This approach not only reduces waste but also leads to cost savings, particularly when using expensive metals.
3. Rapid Prototyping
Metal 3D printing enables rapid prototyping, allowing designers and engineers to quickly create and test prototypes. This speed accelerates the development process, enabling faster time-to-market for new products.
4. Customization
Metal 3D printing allows for high levels of customization. Parts can be tailored to meet specific requirements without the need for costly retooling. This capability is particularly beneficial in industries like aerospace and healthcare, where bespoke components are often required.
5. Reduced Inventory
By producing parts on-demand, metal 3D printing can help companies reduce their inventory costs. There is no need to stockpile large quantities of parts when they can be produced as needed.
The Cons of Metal 3D Printing
1. High Initial Costs
The initial investment in metal 3D printing technology can be high. This includes the cost of the printers, materials, and training for staff. For small and medium-sized enterprises, this upfront cost can be a significant barrier.
2. Material Limitations
Not all metals can be used in 3D printing. The range of materials available for metal 3D printing is expanding, but it is still limited compared to traditional manufacturing. Additionally, the properties of 3D-printed metals can differ from those of traditionally manufactured metals, which can affect performance.
3. Post-Processing Requirements
Parts produced by metal 3D printing often require post-processing, such as heat treatment or surface finishing, to achieve the desired properties and finish. This additional step can add time and cost to the manufacturing process.
4. Speed and Scalability
While metal 3D printing is excellent for prototyping and small-batch production, it may not be as efficient for large-scale manufacturing. Traditional manufacturing methods can produce large quantities of parts more quickly and at a lower cost.
5. Regulatory and Quality Concerns
In industries with strict regulatory requirements, such as aerospace and medical, ensuring the quality and consistency of 3D-printed parts can be challenging. Meeting these standards requires rigorous testing and validation processes.
Comparing Metal 3D Printing with Traditional Manufacturing
To fully appreciate the pros and cons of metal 3D printing, it’s helpful to compare it with traditional manufacturing methods. Traditional methods like CNC machining, casting, and forging have been refined over decades and are highly efficient for mass production. However, they lack the flexibility and customization capabilities of 3D printing.
Cost-Effectiveness of Metal 3D Printing
According to a detailed analysis from Roboze, one of the notable advantages of 3D printing technology is its cost-effectiveness for certain types of production. Traditional manufacturing methods can be cost-prohibitive for small batch production due to the high setup and tooling costs. In contrast, 3D printing has lower initial setup costs, making it more economical for producing small quantities of parts. Additionally, 3D printing significantly reduces the time required to bring a product from concept to market.
By eliminating the need for tooling and molds, manufacturers can quickly iterate on designs and start production faster. Furthermore, 3D printing excels at producing complex parts in a single build process, reducing both cost and production time. The additive nature of 3D printing also ensures material efficiency, minimizing waste and reducing material costs. Lastly, the flexibility of 3D printing allows manufacturers to easily switch between different products without the need for extensive retooling, making it ideal for meeting varying customer demands.
Conclusion: Is Metal 3D Printing Good or Bad?
The answer to whether metal 3D printing is good or bad depends largely on the application. For industries requiring high customization, rapid prototyping, and complex geometries, metal 3D printing offers unparalleled advantages. However, for large-scale production of standardized parts, traditional manufacturing methods may still be more efficient and cost-effective.
Metal 3D printing is a powerful tool in the modern manufacturing arsenal, offering unique capabilities that can complement traditional methods. As technology advances and costs decrease, its adoption is likely to grow, making it an increasingly viable option for a broader range of applications.
By understanding both the benefits and limitations of metal 3D printing, businesses can make informed decisions about integrating this technology into their manufacturing processes. Whether it’s for innovative designs, reduced waste, or rapid prototyping, metal 3D printing holds significant potential for those willing to invest in its capabilities.
References
- 3DEO – Pros and Cons of 3D Printing Metal Components
- TWI Global – Pros and Cons of 3D Printing
- The Steel Printers – Metal 3D Printing: The Benefits and Drawbacks
- AMFG – Metal 3D Printing: A Definitive Guide
- Xometry – 3D Printing Pros and Cons
- Spunky Print – Are Metal 3D Printers Worth It?
- Roboze – Additive Manufacturing vs Traditional Manufacturing: Cost and Advantages of 3D Printing Technology

certainly like your web-site however you need to check the speling on quite a few of your posts.
Many of them are rife with spelling issues and I to find it very troublesome to inform the reality nevertheless I’ll
certainloy clme again again. https://evolution.org.ua/